This blog provides you the basic knowledge about GraphQL Endpoint and how to create it in Magento 2. Let's get started!
What is GraphQL?
GraphQL is a query language for the API, allowing clients to accurately identify the data needed and the server returns only the data requested.
GraphQL compared to REST API
- REST API defines resource information on the server, the client makes the call only. GraphQL allows clients to upload a datasheet, server actions must return the same information.
- The GraphQL server only needs a single endpoint and accurately responds to the data requested by the client, instead of having multiple endpoints, each endpoint returns a fixed data structure as in REST.
What's the GraphQL in Magento?
Graphql was introduced with Magento version 2.3 as an alternative to REST/SOAP API for frontend development.
Magento uses 2 types of GraphQL operations:
- Query: used to read data
- Mutation: used to write data to server
As of version 2.3.4, the following core modules are using GraphQL query language:
- CatalogInventoryGraphQl
- CatalogUrlRewriteGraphQl
- BundleGraphQl
- CatalogGraphQl
- ConfigurableProductGraphQl
- CustomerGraphQl
- DownloadableGraphQl
- EavGraphQl
- GroupedProductGraphQl
- TaxGraphQl
- ThemeGraphQl
- UrlRewriteGraphQl
- WeeeGraphQl
Example: Getting customer information using GraphQl
In this example, we’ll create a simple GraphQL API query to fetch customer information via their email.
Step 1: Create your module
Let's call our module Magenest/GraphQl. Our module must be loaded after GraphQL and Customer module, so the module.xml file would look like this:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<config xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="urn:magento:framework:Module/etc/module.xsd">
<module name="Magenest_GraphQl" >
<sequence>
<module name="Magento_Customer"/>
<module name="Magento_Authorization"/>
<module name="Magento_GraphQl"/>
</sequence>
</module>
</config>
Step 2: Define schema
GraphQL queries are declared under vendor/module/etc/schema.graphqls:
type Query {
testcustomer(
email: String @doc(description: "email of the customer")
): Testcustomer
@resolver(class:"Magenest\\GraphQl\\Model\\Resolver\\Customer")
@doc(description:
"The testcustomer query returns information about a customer")
@cache(cacheable: false)
}
type Testcustomer @doc(description: "Testcustomer defines the customer name and other details") {
entity_id: Int
firstname: String
lastname: String
email: String
}
- “type Query”: declares Query operations of our module
- “testcustomer”: name of our query
- email: String : declares input name (‘email’) and type (‘string)
- Testcustomer : defines identity of the query, including resolver (@resolver) class, document (@doc), is the result cacheable (@cache), etc.
- Here we have defined “cacheable: false” meaning the result will not be cached. If the result can be cached, use @cache tag and define a caching class instead.
- “type Testcustomer” : define the result object of the query, including their name and type
Step 3: Create resolver class for schema in Magento 2
We need to create a resolver model class following the schema definition. Through this method, we simply return data of customers with the requested email.
app/code/Magenest/GraphQl/Model/Resolver/Customer.php
<?php
namespace Magenest\GraphQl\Model\Resolver;
use Magento\Authorization\Model\UserContextInterface;
use Magento\Framework\GraphQl\Schema\Type\ResolveInfo;
use Magento\Framework\Exception\NoSuchEntityException;
use Magento\Framework\Exception\LocalizedException;
use Magento\Framework\GraphQl\Config\Element\Field;
use Magento\Framework\GraphQl\Exception\GraphQlAuthorizationException;
use Magento\Framework\GraphQl\Exception\GraphQlNoSuchEntityException;
use Magento\Framework\GraphQl\Query\Resolver\ContextInterface;
use Magento\Framework\GraphQl\Query\Resolver\Value;
use Magento\Framework\GraphQl\Query\Resolver\ValueFactory;
use Magento\Framework\GraphQl\Query\ResolverInterface;
use Magento\Customer\Model\CustomerFactory;
use Magento\Customer\Api\CustomerRepositoryInterface;
use Magento\Customer\Api\Data\CustomerInterface;
use Magento\Framework\Webapi\ServiceOutputProcessor;
use Magento\Framework\Api\ExtensibleDataObjectConverter;
/**
* Customers field resolver, used for GraphQL request processing.
*/
class Customer implements ResolverInterface
{
/**
* @var ValueFactory
*/
private $valueFactory;
/**
* @var CustomerFactory
*/
private $customerFactory;
/**
* @var ServiceOutputProcessor
*/
private $serviceOutputProcessor;
/**
* @var ExtensibleDataObjectConverter
*/
private $dataObjectConverter;
/**
* @var \Psr\Log\LoggerInterface
*/
private $logger;
/**
*
* @param ValueFactory $valueFactory
* @param CustomerFactory $customerFactory
* @param ServiceOutputProcessor $serviceOutputProcessor
* @param ExtensibleDataObjectConverter $dataObjectConverter
*/
public function __construct(
ValueFactory $valueFactory,
CustomerFactory $customerFactory,
ServiceOutputProcessor $serviceOutputProcessor,
ExtensibleDataObjectConverter $dataObjectConverter,
CustomerRepositoryInterface $customerRepository,
\Psr\Log\LoggerInterface $logger
) {
$this->valueFactory = $valueFactory;
$this->customerFactory = $customerFactory;
$this->serviceOutputProcessor = $serviceOutputProcessor;
$this->dataObjectConverter = $dataObjectConverter;
$this->customerRepository = $customerRepository;
$this->logger = $logger;
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function resolve(Field $field, $context, ResolveInfo $info, array $value = null, array $args = null) {
if (!isset($args['email'])) {
throw new GraphQlAuthorizationException(
__(
'email for customer should be specified',
[\Magento\Customer\Model\Customer::ENTITY]
)
);
}
try {
$data = $this->getCustomerData($args['email']);
$result = function () use ($data) {
return !empty($data) ? $data : [];
};
return $this->valueFactory->create($result);
} catch (NoSuchEntityException $exception) {
throw new GraphQlNoSuchEntityException(__($exception->getMessage()));
} catch (LocalizedException $exception) {
throw new GraphQlNoSuchEntityException(__($exception->getMessage()));
}
}
/**
*
* @param int $context
* @return array
* @throws NoSuchEntityException|LocalizedException
*/
private function getCustomerData($customerEmail) : array
{
try {
$customerData = [];
$customerColl = $this->customerFactory->create()->getCollection()->addFieldToFilter('email', ['eq'=>$customerEmail]);
foreach ($customerColl as $customer) {
array_push($customerData, $customer->getData());
}
return isset($customerData[0])?$customerData[0]:[];
} catch (NoSuchEntityException $e) {
return [];
} catch (LocalizedException $e) {
throw new NoSuchEntityException(__($e->getMessage()));
}
}
}
Couple of things to note:
- Resolver class must implement
Magento\Framework\GraphQl\Query\ResolverInterface - “resolve” is the main method of this class, with $args as the query’s input
- GraphQL has several exception classes, including
GraphQlAuthorizationExceptionandGraphQlNoSuchEntityException. These must be used to return the error to the client
Testing
You can check your GraphQL query and response by installing a Chrome extension called “ChromeiQL”. Then, set the endpoint as “<your magento root url>/graphql”.
After that, input your GraphQL query on the left side of “ChromeiQL” interface and click on the “Set endpoint” button. For a correct email address, the query result will be as the following:
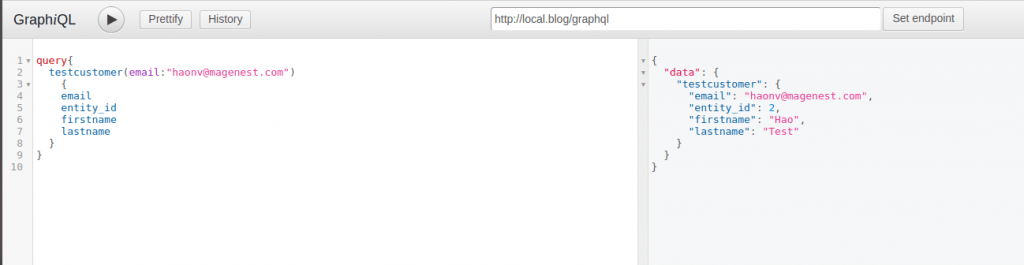
You can find the source code for our example module here.
Thank you for reading!




![How to create a new product type in Magento 2 [Step-by-Step]](https://store.magenest.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/create-a-new-product-type-in-magento-2.jpg)











Simple and very easy to understand. Thanks :)
minor issue :
vendor/module/etc/shema.graphqls please correct schema.graphqls in this page : https://store.magenest.com/blog/create-graphql-endpoint-in-magento-2/
I spent 20 mins to find this issue
{
"errors": [
{
"message": "Cannot query field \"testcustomer\" on type \"Query\".",
"extensions": {
"category": "graphql"
},
"locations": [
{
"line": 33,
"column": 3
}
]
}
]
}